Envetec Insight
The Hidden Cost of Biohazardous Waste: Expanding Scope 3 Emissions in Life Sciences
Waste isn’t often the first thing that comes to mind when considering sustainability in life sciences. However, biohazard waste and regulated medical waste significantly contribute to the industry’s carbon footprint, especially through Scope 3 emissions. These indirect emissions across the value chain are already 5.4 to 6.5 times higher than Scope 1 and 2 emissions combined in biotech and pharma, as highlighted in My Green Lab’s 2024 report. Understanding this impact is crucial for improving sustainability in the life sciences sector. This post explores how waste expands Scope 3 emissions and offers actionable solutions for mitigation.
Understanding Scope 3 Emissions in the Life Sciences Industry
Scope 3 emissions are indirect emissions from activities not directly controlled by a company. These include:
- Purchased goods and services
- Waste generated in operations
- End-of-life treatment of sold products
In life sciences, Scope 3 emissions often dominate the carbon footprint due to waste management practices like incineration and thermal treatment, which are energy-intensive processes.
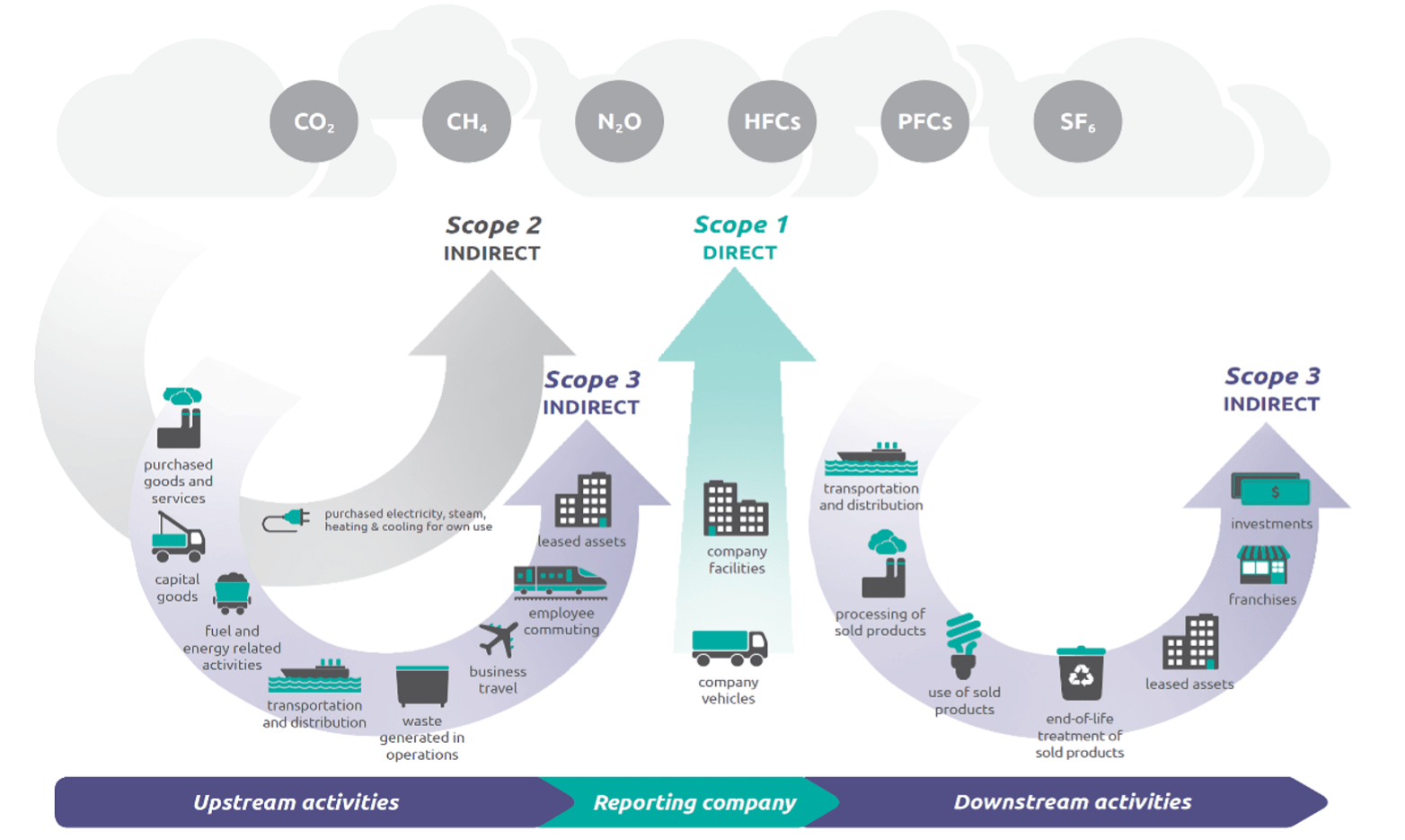
(Source: https://ghgprotocol.org/sites/default/files/standards/Corporate-Value-Chain-Accounting-Reporing-Standard_041613_2.pdf)
How Waste Management Expands Scope 3 Emissions
Biohazardous and regulated medical waste, including contaminated plastics, sharps, and other materials, contributes to Scope 3 emissions in several ways:
- Transportation Emissions: Transporting biohazard waste to off-site treatment facilities often involves long distances, increasing emissions from fossil fuel use.
- Energy-Intensive Treatment Methods: Common biohazard waste treatment methods like incineration and autoclaving consume significant energy and release greenhouse gases.
- Lack of Recycling in Waste Treatment: Traditional thermal methods make waste unsuitable for recycling. Since the waste is destroyed or altered, it cannot be reintroduced into the supply chain.
These challenges increase emissions, hinder sustainability goals, and create reporting issues for companies subject to regulations like the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD).
Sustainable Waste Management Solutions for Biohazard Waste
Reducing waste-related Scope 3 emissions requires innovative approaches to waste treatment. Here are three key strategies:
- On-Site Waste Treatment: Treating clinical waste collection at its source eliminates long-distance transportation, significantly reducing emissions.
- Non-Thermal Disinfection Methods: Using non-thermal processes for biohazard waste treatment lowers energy consumption while effectively neutralising biohazards.
- Enabling Biohazardous Waste Recycling: Transforming treated biohazardous materials into recyclable forms allows reintroduction into supply chains, supporting a circular economy. Prioritising these strategies can mitigate the environmental impact of waste while maintaining safety and compliance.
Broader Impacts of Addressing Waste in Scope 3 Emissions
Addressing waste-related emissions in life sciences offers benefits beyond carbon reduction:
- Cost Savings: Minimising transport and energy use lowers operational costs associated with waste treatment.
- Regulatory Compliance: Sustainable waste management aligns with increasingly stringent emissions regulations.
- Reputation Management: Greener practices enhance credibility with stakeholders.

Conclusion: Waste Recycling as a Sustainability Solution
Biohazardous waste plays a significant role in Scope 3 emissions, but it also presents an opportunity for positive change. By adopting sustainable waste management practices, including biohazardous waste recycling and waste treatment, the life sciences industry can reduce its environmental footprint while promoting innovation and circularity.
Waste is no longer just a by-product; it’s a crucial part of the sustainability puzzle. Through collective action and innovative strategies, waste management can become a cornerstone of climate-conscious operations.
Previous article