Currently, all biohazardous waste is autoclaved, incinerated and mostly landfilled.
This process emits huge amounts of CO2 and other greenhouse gases, uses vast amounts of water and is incredibly damaging to the environment. According to Health Care Without Harm, the healthcare sector alone contributes 4.4% of global emissions, and that footprint is forecast to triple by 2050. Something has to change.
Envetec is that change.
GENERATIONS is a novel onsite technology that simultaneously shreds and disinfects biohazardous waste at source
The onsite process features:
- Non-thermal treatment
- Low energy usage
- Low water usage
- An organic biodegradable treatment compound
Because of the novel nature of this process treated waste can be diverted from incineration and landfill as GENERATIONS act as an essential link in the chain for recycling of biohazardous waste.
- The process is simple but is backed up by complex engineering and 10 years of R&D.
How it Works
Human Machine Interface
Powered by Siemens Insights Hub our intuitive HMI is the brain of the GENERATIONS technology. The user friendly interface can initiate a treatment cycle in three clicks, detect and communicate issues and capture real time data for remote diagnostics and carbon reporting.

Receiver
The heart of the GENERATIONS unit. The entire treatment process, both shredding and disinfection take place in the receiver. The receiver is dynamic and automatically adjusts position for ease of loading and to release treated material post cycle.
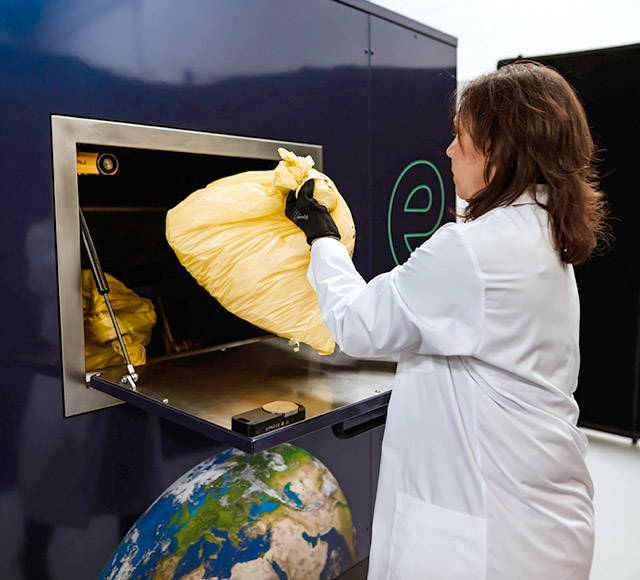

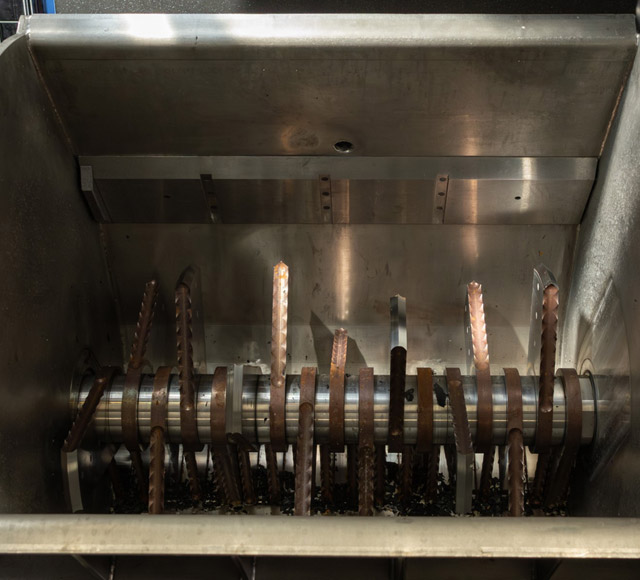
Blades
GENERATIONS robust blade system is designed specifically to shred biohazardous/regulated medical waste. The smart blade system assess resistance of a waste load at the beginning of every cycle to determine the optimal power output required for shredding and ensure that material placed in the receiver is suitable for shredding.

Chemical
GENERATIONS utilises an organic, biodegradable chemical to achieve STAATT IV (6log10) inactivation of microbes. Post treatment the chemical breaks down into ethanoic acid and water.

Validation System
This novel validation system validates the efficacy of the GENERATIONS process during live waste processing ensuring the highest level of confidence in the efficacy.
Auger
Post treatment this dewatering auger receives treated material and separates solid from effluent. Pushing treated solid material into a receptacle and sending effluent to the GENERATIONS filtration system.

Neutralisation & Filtration
Depending on material being treated neutralizer may be dosed to ensure a PH that is acceptable for effluent and solid material. PH balanced effluent is sent to the GENERATIONS filtration unit where it is filtered removing any visible solids and microplastics.

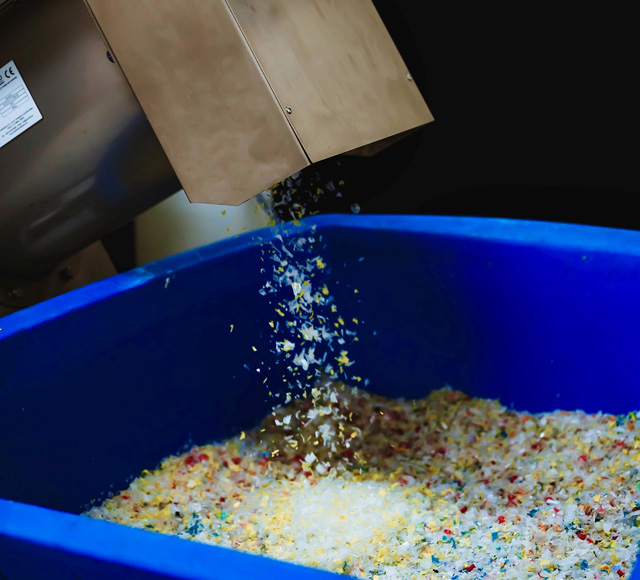
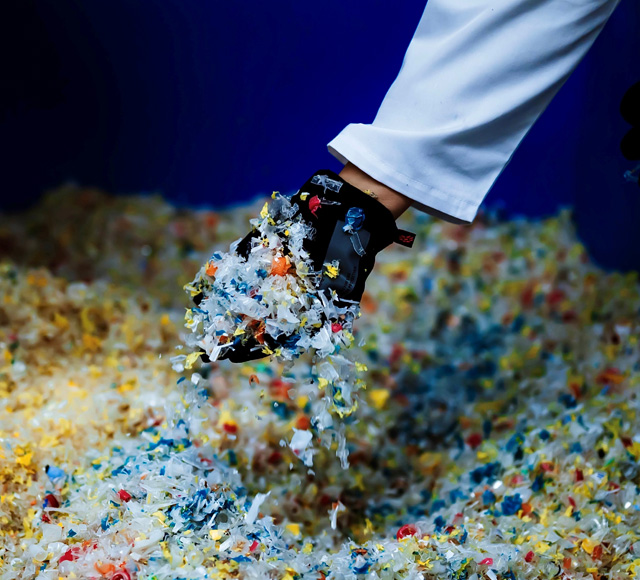
Flake
Treated polymer flake dispensed in the receptacle can now be collected and sent to a material recycling facility for separation and pelletisation.

Benefits of Our Technology
Industries We Serve
Biohazardous waste, generated from healthcare facilities such as hospitals, laboratories, and research centres, poses a significant and serious challenge within the waste sector. This category of waste creates unique challenges due to its biohazardous nature, prompting stringent regulations governing its management and treatment. The treatment of biohazardous waste is a critical aspect of waste management, primarily driven by the need to protect public health and the environment from potential harm. Globally, the handling of biohazardous waste is governed by a framework of stringent regulations. International bodies, such as the World Health Organization (WHO, 2018) and the Basel Convention (1989), establish guidelines to ensure the safe and responsible management of biohazardous waste. These regulations encompass the entire waste management process, from collection to treatment and disposal, with a focus on preventing the spread of infections and safeguarding environmental and public health. Compliance with these global standards is crucial for mitigating the risks associated with biohazardous waste and promoting consistent, safe practices across diverse healthcare and research settings worldwide.
The treatment of biohazardous waste typically involves processes that, while effective, are notably emissions-intensive compared to the treatment of general waste. Incineration, a prevalent method, releases various pollutants into the atmosphere, including greenhouse gases, it also contains potentially harmful chemicals and eliminates possibilities for recycling. The high temperatures required for complete waste destruction contribute the majority of the environmental footprint of this process. The search for more ecologically friendly solutions becomes critical given the effects standard treatment procedures have on the environment. As facilities are increasingly prioritising sustainability, the biomedical and healthcare industries are compelled to explore innovative technologies and methods that mitigate the environmental consequences of biohazardous waste treatment. Balancing the need for efficacy with reduced emissions is at the forefront of this paradigm shift.
These actions are in line with the Health Service Executive (HSE) in Ireland, a public healthcare body, decarbonisation plans to become net zero energy related emissions by 2050 (HSE Infrastructure Decarbonisation Roadmap, 2021). This decarbonisation plan is in line with the Irish Government’s Climate Action Plan 2021 (Irish Government, 2021). 2 of the 10 points in the HSE Climate Action plan are focused on Waste and Water. For waste, their goal is to reduce clinical risk waste and to increase recycling.
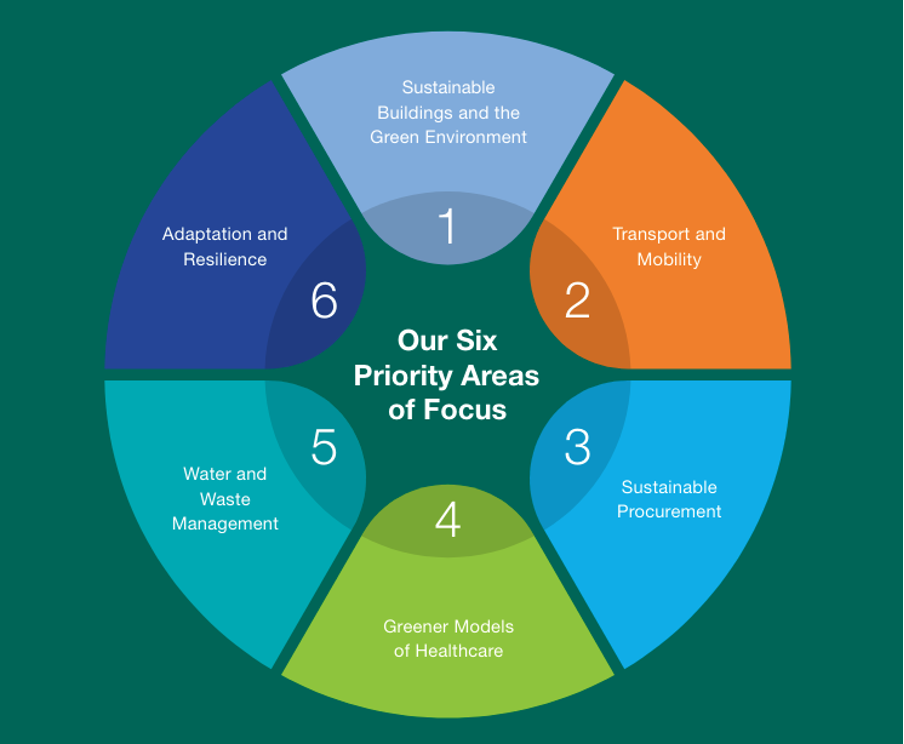
(HSE Six Priority Areas of Focus, HSE Climate Action Plan, 2023)
Separately in the UK, the NHS has possibly the most ambitious plans for NetZero and are leading the charge on sustainability initiatives. In March 2023, the NHS issued a new Clinical Waste Strategy. The strategy sets out NHS England’s ambition to transform the management of clinical waste by eliminating unnecessary waste, finding innovative ways to reuse, and ensure waste is processed in the most cost effective, efficient, and sustainable way. The strategy emphasises the need to move towards onsite treatment of biohazardous waste and specifically states that the plan is: “Enabling NHS ownership and control of its own processing assets, including making use of innovative technologies to treat infectious waste on-site”. This eliminates all biohazardous waste leaving the facility.
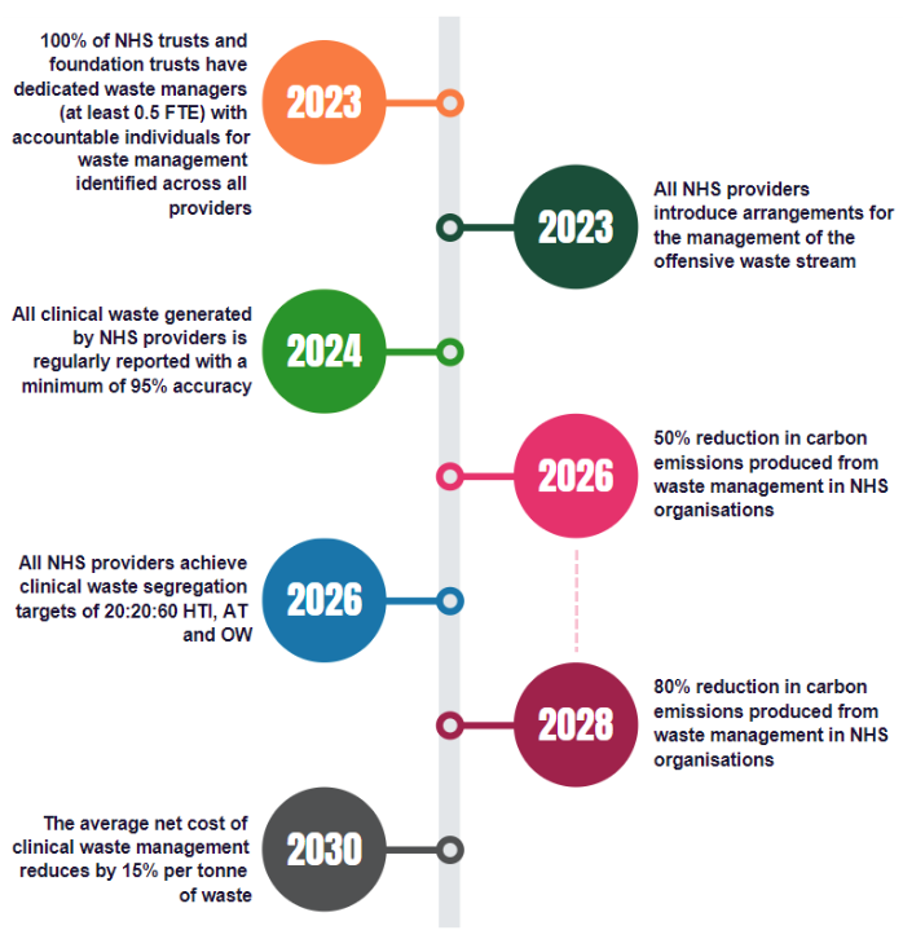
(NHS Clinical Wast Sustainability Roadmap, 2023)
(Source: https://www.england.nhs.uk/long-read/nhs-clinical-waste-strategy/)
There is a growing international call for a new disruptive technology that would work effectively and be economically beneficial at the same time. By aligning the environmental interests of the planet, with the economic interest of the stakeholders, the sustainability effort can itself, become sustainable.
GENERATIONS is helping the largest private hospital group in New York State treat their regulated medical waste sustainably and can also help your healthcare facility to achieve its sustainability goals.
90% of public pharma and companies analyzed in the sector still do not have emission reduction targets in the short-term (2021 – 2025) that are aligned with a 1.5°C increase world. The pharmaceutical industry generates substantial volumes of biohazardous waste as a byproduct of research, development, and manufacturing activities. This category of waste, which includes infectious materials, toxins, and other hazardous substances, presents unique challenges that necessitate stringent management protocols to safeguard public health and the environment.
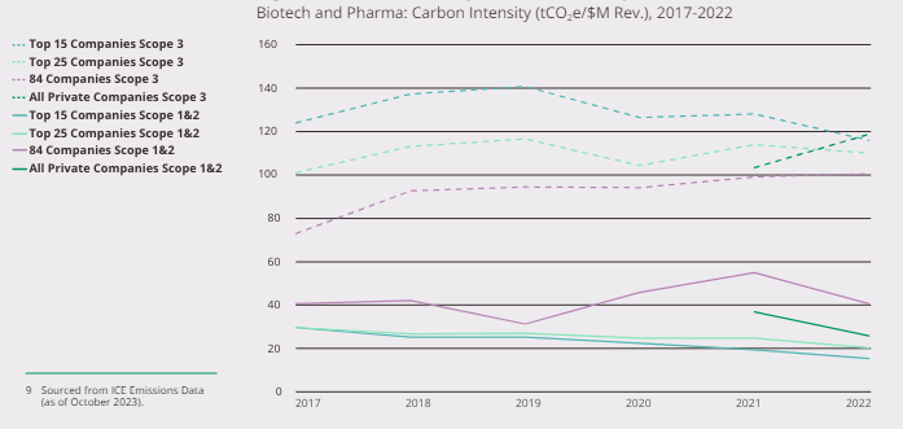
(6-Year Pharma & Biotech Industry Carbon Intensity Trends, ICE Emissions Data, 2023)
Internationally, the handling of biohazardous waste is governed by a comprehensive regulatory framework established by organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) whose “Laboratory Biosafety Manual” serves as a key guideline. The Basel Convention also plays a crucial role, with its Annex I, II, and III classifications (https://www.basel.int/TheConvention/Overview/tabid/1271/Default.aspx) categorizing different waste types to ensure proper management.
Traditionally, the treatment of biohazardous waste has relied heavily on incineration, a process that effectively neutralizes the hazardous properties of the waste but contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. A study by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (https://www.epa.gov/stationary-sources-air-pollution) highlights the impact of incineration on air quality and greenhouse gas emissions. As the industry increasingly prioritizes sustainability and environmental stewardship, there is a pressing need to explore alternative technologies that offer both efficacy and reduced environmental impact.
The pharmaceutical sector’s commitment to sustainability aligns with global initiatives aimed at reducing the carbon footprint of industrial operations. For instance, the European Union’s Pharmaceutical Strategy for Europe (2020) emphasizes the importance of minimizing the environmental impact of pharmaceutical manufacturing, including the responsible management of waste streams.
Furthermore, individual countries are implementing ambitious decarbonization plans that directly impact the pharmaceutical industry. In the United Kingdom, the National Health Service (NHS) has set a goal of achieving net-zero emissions by 2040, with a particular focus on reducing single-use plastics and improving waste management practices. The NHS’s “Clinical Waste Strategy” specifically calls for the adoption of innovative technologies to enable on-site treatment of biohazardous waste, reducing the need for transportation and off-site incineration.
The transition to more sustainable biohazardous waste management practices not only aligns with environmental objectives but also presents economic opportunities for pharmaceutical companies. By embracing innovative technologies that enable the recovery and reuse of valuable materials from waste streams, companies can realize cost savings. For example, recovering high value polymers from what is typically considered waste can significantly reduce the need for purchasing virgin materials, improving resource efficiency. This approach contributes to the development of a circular economy.
As pharmaceutical facilities prioritize sustainability, the adoption of disruptive technologies like our GENERATIONS system becomes essential. GENERATIONS offers an innovative solution for treating biohazardous waste on-site, reducing transportation needs and eliminating off-site incineration. This eliminates all biohazardous waste leaving the facility. This approach not only cuts greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution but also promotes resource efficiency by recovering valuable materials from waste streams. By integrating GENERATIONS into their waste management practices, pharmaceutical companies can lead the way towards a sustainable future, safeguarding the environment and enhancing long-term business resilience.
The Mounting Challenge of Single-Use Plastics in Medtech
The medtech industry, encompassing device manufacturers, hospitals, and healthcare facilities, faces a growing challenge: the environmental impact of single-use plastics. From packaging to vital equipment, these plastics are prevalent but contribute significantly to pollution, resource depletion, and carbon emissions [https://noharm-europe.org/issues/europe/towards-plastic-free-healthcare-europe]. A 2021 study published in Health Care Without Harm Europe found that medical consumables, largely plastic, can make up over 80% of a hospital’s daily waste by weight.
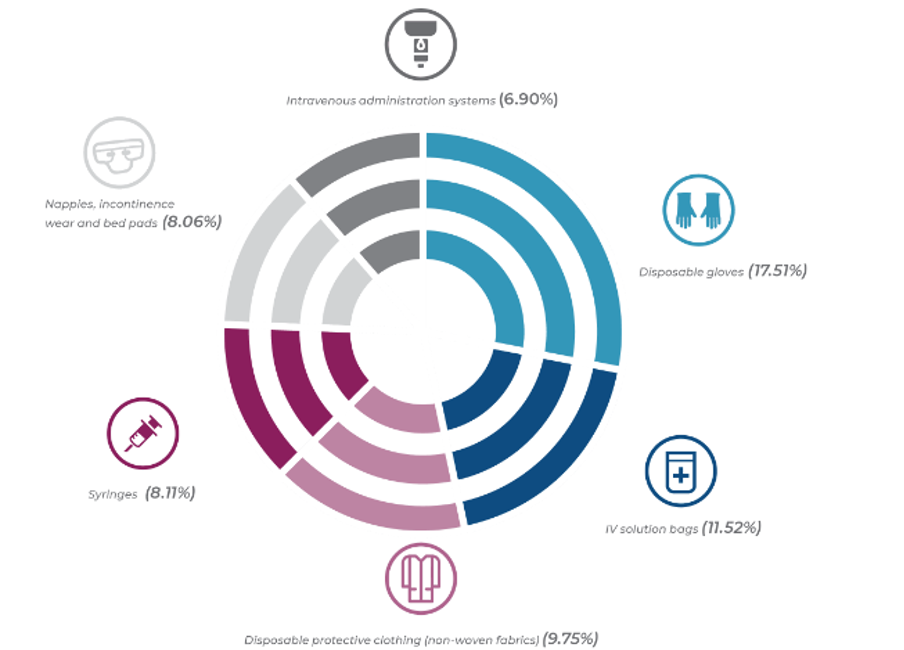
(Common examples of disposable medical devices for in clinical wate, HCWH, 2021)
(Source: https://europe.noharm.org/towards-plastic-free-healthcare-europe)
Shifting Tides: Sustainability Efforts
Fortunately, there’s a growing movement towards sustainable practices. Industry groups like MedTech Europe advocate for eco-friendly alternatives and waste reduction across the supply chain. Their efforts might involve promoting a circular economy for medical plastics, where materials are kept in use for as long as possible. This could involve:
- Reprocessing used plastics into new medical supplies.
- Redesigning products to be durable and reusable.
- Implementing take-back programs for used medical devices.
- Government Regulations and Incentives
Regulatory bodies are also taking action. Policies promoting sustainable materials, recycling, and waste reduction are being introduced. Additionally, incentives like tax breaks for developing sustainable design can further encourage innovation [https://www.washingtonpost.com/opinions/2023/06/15/health-care-hospitals-plastics-reusable-environment/].
End Users Leading the Charge
Healthcare organizations are aligning with broader sustainability goals. Initiatives like Ireland’s HSE decarbonization plans and the UK’s NHS Clinical Waste Strategy highlight the importance of responsible waste management.
The NHS strategy, for example, emphasizes eliminating unnecessary waste, promoting reuse, and exploring innovative on-site treatment technologies for biohazardous waste [https://www.england.nhs.uk/estates/nhs-clinical-waste-strategy/]. This eliminates all biohazardous waste leaving the facility and empowers healthcare facilities to manage their waste efficiently and cost-effectively, while minimizing environmental impact.
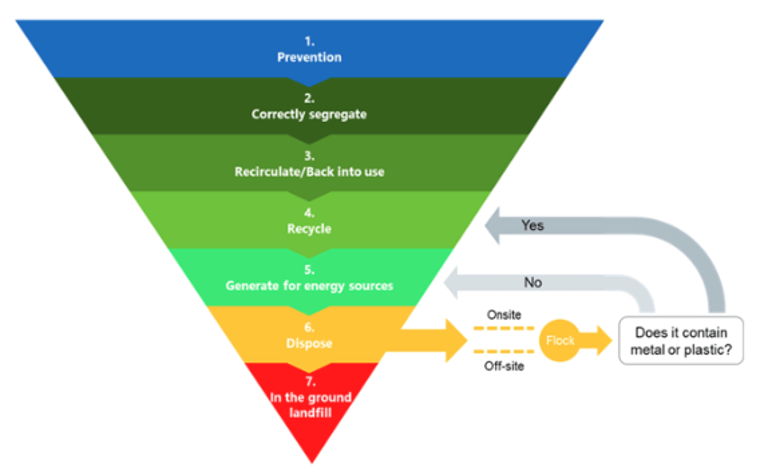
(Clinical Waste Hierarchy, 2023)
(Source: https://www.england.nhs.uk/long-read/nhs-clinical-waste-strategy/)
Disruptive Technologies for a Circular Economy
The need for disruptive solutions is clear. Technologies like GENERATIONS that address the environmental challenges of single-use plastics, while aligning with economic interests, are crucial. Ending the terminal supply chain for these high value polymers is essential.
Collaboration is Key
Through collaboration between industry, government, and technology providers, the medtech sector can achieve a sustainable future. By prioritizing environmental preservation alongside economic prosperity, we can create a circular economy where waste is minimized and resources are used efficiently.
Contact us to learn how GENERATIONS can help your facility transition to a sustainable biohazardous waste management solution, reducing environmental impact while unlocking economic opportunities through the circular economy.
Sustainable Biohazardous Waste Management in the Food & Beverage Industry
The Food & Beverage industry plays a vital role in ensuring the safety, quality, and availability of food products for consumers worldwide. However, the activities associated with food production, processing, and quality control generate significant volumes of biohazardous waste, posing potential risks to public health and the environment if not managed properly.
Biohazardous waste in the Food & Beverage context encompasses a wide range of materials, including infectious substances, sharps, pathological waste, and contaminated products. This waste is generated not only during manufacturing processes but also in the industry’s extensive laboratory operations, where research, development, and quality testing take place.
While the mishandling or improper disposal of biohazardous waste can lead to the spread of foodborne illnesses and environmental contamination, the impact of traditional disposal methods on the environment is also extremely detrimental.
Globally, the management of biohazardous waste is subject to stringent regulations and guidelines set forth by organizations such as the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the Basel Convention. These frameworks aim to ensure the safe and responsible handling, treatment, and disposal of biohazardous materials, safeguarding both human health and the environment.
Traditionally, the treatment of biohazardous waste in the Food & Beverage industry has relied heavily on incineration, a process that effectively neutralizes the hazardous properties of the waste but contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. As the industry increasingly embraces sustainable practices, there is a growing demand for alternative technologies that offer both efficacy and reduced environmental impact. These technologies such as GENERATIONS can enable novel supply chains for this waste, especially given the standardized nature of Food & Beverage testing apparatus. The below demonstrates a recycling process tested by Envetec for one of our Dairy clients, which focused on their most common waste stream, agar plates:

The Food & Beverage industry’s commitment to sustainability aligns with global initiatives aimed at reducing the carbon footprint of industrial operations and promoting a circular economy. For instance, the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) emphasize the importance of sustainable food production systems and responsible consumption and production patterns.
Furthermore, individual countries are implementing ambitious decarbonization plans that directly impact the Food & Beverage industry. In the European Union, the Farm to Fork Strategy (2020) calls for a transition to a sustainable food system, including the responsible management of waste streams and the reduction of environmental impacts along the entire supply chain.
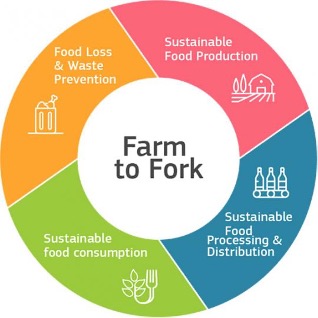
(EU Farm to Fork Strategy target areas, 2024)
(Source: https://food.ec.europa.eu/horizontal-topics/farm-fork-strategy_en)
The transition to more sustainable biohazardous waste management practices in the Food & Beverage industry not only aligns with environmental objectives but also presents economic opportunities. By embracing innovative technologies that enable the recovery and reuse of valuable materials from waste streams, facilities can realize cost savings, improve resource efficiency, and contribute to the development of a circular economy.
As the Food & Beverage industry continues to prioritize sustainability and responsible waste management, the adoption of disruptive technologies that effectively treat biohazardous waste while minimizing environmental impact will become increasingly essential. By aligning environmental stewardship with economic interests, the industry can foster a sustainable approach to biohazardous waste management that safeguards public health, protects the environment, and supports long-term business resilience.
Contact us to learn how GENERATIONS can help your Food & Beverage facility transition to a sustainable biohazardous waste management solution, reducing environmental impact while unlocking economic opportunities through the circular economy and simultaneously eliminating the need to transport biohazardous waste from your facility.
The veterinary science industry plays a crucial role in safeguarding animal health and welfare, as well as ensuring the safety of the food supply chain. However, the activities associated with veterinary care, research, and animal husbandry generate significant volumes of biohazardous waste, posing potential risks to public health and the environment if not managed properly.
Biohazardous waste in the veterinary context encompasses a wide range of materials, including infectious substances, sharps, pathological waste, and animal carcasses. The mishandling or improper disposal of these materials can lead to the spread of zoonotic diseases, environmental contamination, and the release of harmful pathogens into the ecosystem.
Globally, the management of biohazardous waste is subject to stringent regulations and guidelines set forth by organizations such as the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) and the Basel Convention. These frameworks aim to ensure the safe and responsible handling, treatment, and disposal of biohazardous materials, safeguarding both human and animal health while minimizing environmental impacts.
Traditionally, the treatment of veterinary biohazardous waste has relied heavily on incineration, a process that effectively neutralizes the hazardous properties of the waste but contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. As the industry increasingly embraces sustainable practices, there is a growing demand for alternative technologies that offer both efficacy and reduced environmental impact.
The veterinary science industry’s commitment to sustainability aligns with global initiatives aimed at reducing the carbon footprint of industrial operations and promoting a circular economy. For instance, the European Union’s Farm to Fork Strategy (2020) emphasizes the importance of sustainable food production systems, including responsible waste management practices along the entire supply chain.
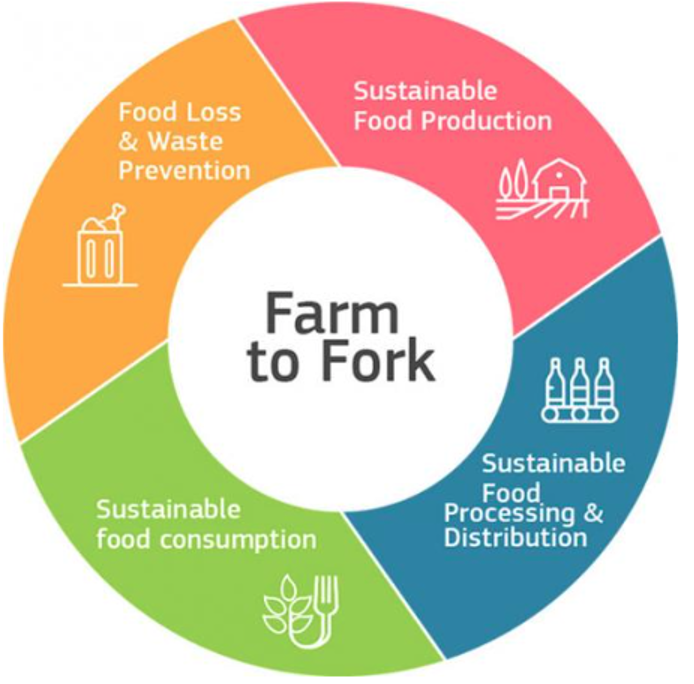
(EU Farm to Fork Strategy target areas, 2024)
(Source: https://food.ec.europa.eu/horizontal-topics/farm-fork-strategy_en)
Furthermore, individual countries are implementing ambitious decarbonization plans that directly impact the veterinary science industry. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established the AgStar program, which encourages the adoption of sustainable waste management practices in animal agriculture, including the recovery and utilization of biogas from animal waste.
The transition to more sustainable biohazardous waste management practices in the veterinary science industry not only aligns with environmental objectives but also presents economic opportunities. By embracing innovative technologies that enable the recovery and reuse of valuable materials from waste streams, facilities can realize cost savings, improve resource efficiency, and contribute to the development of a circular economy.
As the veterinary science industry continues to prioritize sustainability and responsible waste management, the adoption of disruptive technologies that effectively treat biohazardous waste while minimizing environmental impact will become increasingly essential.
Contact us to learn how GENERATIONS can help your veterinary facility transition to a sustainable biohazardous waste management solution, reducing environmental impact while unlocking economic opportunities through the circular economy and simultaneously eliminating the need to transport biohazardous waste from your facility.